What Are PFAS? Understanding Their Impact on the Environment, Health, and Industry
The Hidden Danger: Why You Should Care About PFAS
Imagine drinking a glass of water, thinking it’s pure and safe—only to discover invisible chemicals inside it that could stay in your body forever. This isn’t science fiction; it’s the reality of PFAS, a group of chemicals found in everything from waterproof clothing to fast-food packaging. These “forever chemicals” don’t break down easily, leading to long-term accumulation in water, soil, and living organisms. This persistence poses serious risks to the environment, human health, and industries worldwide, as PFAS contamination can disrupt ecosystems, increase medical concerns, and create financial burdens for affected industries.
So, what exactly are PFAS, why are they dangerous, and what are governments doing to regulate them?
<Index>
1-1. Definition and Basic Characteristics
1-2. Where Can You Find PFAS?
2. How Do PFAS Affect the Environment?
2-1. Water Contamination
2-2. Impact on Wildlife
2-3. Soil and Air Pollution
3. How Do PFAS Affect Human Health?
3-1. The Health Risks of PFAS Exposure
3-2. How Do People Get Exposed?
4. How Do PFAS Affect the Industry?
4-1. Industrial Impact and Economic Challenges
4-2. Manufacturing and Compliance Costs
4-3. Legal and Reputational Risks
4-4. Innovations in PFAS Alternatives
5-1. How Different Countries Are Responding
5-2. Challenges in Regulation
6. How Can We Reduce PFAS Exposure?
6-1. What You Can Do
7. The Role of Advanced Evaporation Technology
8. Conclusion: The Future of PFAS Management
1. What Are PFAS?
1-1. Definition and Basic Characteristics
PFAS (Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances) are a group of synthetic chemicals used in manufacturing due to their water- and grease-resistant properties. They have been widely used since the 1940s in everyday products like non-stick cookware, water-resistant fabrics, and even firefighting foams.
However, their strength is also their biggest problem: PFAS do not break down in nature, earning them the nickname “forever chemicals.”
1-2. Where Can You Find PFAS?
PFAS are everywhere! They’re in:
- Non-stick pans (Teflon coating)
- Waterproof clothing (like raincoats)
- Fast-food wrappers (grease-resistant coatings)
- Firefighting foam (used at airports and military bases)
- Cosmetics (certain long-lasting makeup products)
Because they don’t easily degrade, they accumulate in soil, water, and even human bodies over time.
2. How Do PFAS Affect the Environment?
2-1. Water Contamination
PFAS can easily enter the environment through industrial waste, firefighting foam runoff, and landfill leaks. Once in the water system, they spread quickly and contaminate drinking water.
Many cities worldwide are now facing serious water contamination issues due to PFAS pollution. Even remote areas are not safe, as PFAS travel through rivers and groundwater.
2-2. Impact on Wildlife
Animals that consume PFAS-contaminated water also absorb these chemicals into their bodies. Studies show that PFAS exposure in wildlife can lead to:
- Reproductive issues
- Developmental problems in young animals
- Changes in immune system function
2-3. Soil and Air Pollution
PFAS can be found in the air and soil as well. When products containing PFAS degrade (such as clothing and packaging), these chemicals leach into the ground and eventually reach crops and livestock. This means that PFAS can even enter our food supply.
3. How Do PFAS Affect Human Health?
3-1. The Health Risks of PFAS Exposure
Research shows that prolonged exposure to PFAS can cause serious health problems, including:
- Cancer: Some PFAS chemicals are linked to kidney and testicular cancer.
- Hormonal Disruptions: PFAS interfere with the endocrine system, which regulates hormones.
- Immune System Weakening: Studies suggest that PFAS reduce the body’s ability to fight infections.
- Liver Damage: Long-term exposure can lead to liver disease.
- Developmental Issues: PFAS can affect children’s growth and development, leading to lower birth weights and delayed puberty.
3-2. How Do People Get Exposed?
People can absorb PFAS through:
- Drinking contaminated water
- Eating food grown in PFAS-contaminated soil
- Using household products containing PFAS
- Inhaling airborne PFAS particles
Since PFAS accumulate in the body over time, even small amounts can be harmful in the long run.
Discover the Smart Evaporator™: The Safer, Simpler Solution for Solvent Removal
4. How Do PFAS Affect the Industry?
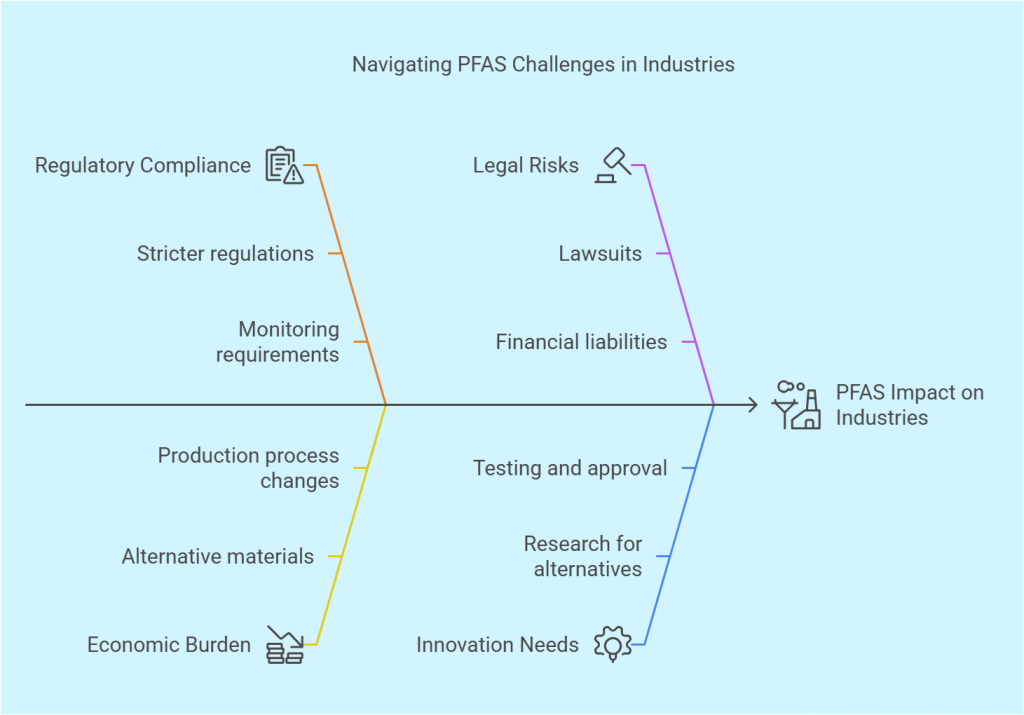
4-1. Industrial Impact and Economic Challenges
Industries that have relied on PFAS for decades are now facing significant regulatory and economic challenges. Sectors such as aerospace, automotive, textiles, food packaging, semiconductors, healthcare, and chemical manufacturing have used PFAS for their unique properties, including water and oil resistance, heat stability, and chemical inertness. The semiconductor industry depends on PFAS for critical manufacturing processes, while the healthcare sector uses PFAS in medical devices and protective equipment. In the chemical industry, PFAS play a role in specialized coatings and formulations. However, growing awareness and stricter regulations are forcing companies across these industries to rethink their reliance on these chemicals and seek sustainable alternatives.
4-2. Manufacturing and Compliance Costs
Many manufacturers are now required to invest in alternative materials and new production processes to comply with emerging PFAS regulations. This transition is costly and time-consuming, as companies must balance maintaining product performance with meeting environmental and health standards. Additionally, regulatory compliance increases operational costs due to mandatory monitoring, reporting, and disposal requirements for PFAS-containing waste.
4-3. Legal and Reputational Risks
Lawsuits against PFAS manufacturers have been increasing, with affected communities and regulatory bodies seeking compensation for environmental cleanup and health damages. Several major legal cases have resulted in multi-billion-dollar settlements over PFAS contamination in water supplies. These legal actions highlight the significant financial and reputational risks associated with PFAS production and pollution. Companies found responsible for PFAS contamination face substantial legal liabilities, which can impact their financial stability and reputation. As a result, industries are under growing pressure to adopt more sustainable practices and demonstrate corporate responsibility.
4-4. Innovations in PFAS Alternatives
To address these challenges, research into PFAS-free alternatives is accelerating. Scientists and engineers are developing new coatings, filtration systems, and treatment technologies to replace PFAS in industrial applications. While these innovations are promising, widespread adoption requires further testing and regulatory approval to ensure safety and effectiveness.
5. Global Regulations on PFAS
5-1. How Different Countries Are Responding
Governments worldwide are beginning to take PFAS contamination seriously. Here’s how different regions are regulating these chemicals:
- United States: The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) is setting new limits for PFAS in drinking water, banning certain PFAS compounds, and funding cleanup projects in contaminated areas. The EPA has also introduced a roadmap to research alternative solutions to PFAS pollution. Additionally, the agency is investing in community awareness programs, ensuring that affected populations have access to information about PFAS contamination and available mitigation strategies. New regulations also require manufacturers to disclose PFAS use in consumer goods, helping consumers make informed choices about exposure risks.
- European Union: The EU is phasing out PFAS use in consumer products and implementing stricter industrial regulations. Some member states, such as Germany and Denmark, have already taken independent actions to ban specific PFAS compounds in food packaging and other goods. The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) has been working on a comprehensive ban covering thousands of PFAS compounds, aiming to eliminate non-essential uses of these chemicals in various industries. In addition, EU member states are investing in advanced PFAS detection technologies, allowing for more precise monitoring of contamination levels in water and soil.
- Japan & South Korea: These countries are conducting extensive PFAS monitoring and developing new water treatment technologies. Japan is focusing on improving filtration methods, investing in research to enhance existing purification systems, and collaborating with universities to explore advanced removal techniques. Meanwhile, South Korea is implementing tighter regulations on industrial PFAS discharge and enforcing stricter monitoring requirements for businesses that produce or handle PFAS-containing products. The South Korean government is also supporting studies to understand long-term PFAS effects on local ecosystems.
- Australia & Canada: Australia has issued guidelines for PFAS levels in drinking water and is investing in research for safer disposal methods. Additionally, the country is exploring the feasibility of a nationwide PFAS cleanup initiative that would target highly contaminated sites. Canada is following a similar approach, with federal and provincial governments working together to restrict PFAS emissions and contamination. Canadian authorities are also funding independent research programs that aim to develop alternative materials to replace PFAS in various industries, reducing the reliance on these persistent chemicals.
- China & India: As major manufacturing hubs, both countries are beginning to implement PFAS monitoring programs and setting restrictions on industrial PFAS emissions, though enforcement remains a challenge. China has introduced new wastewater treatment standards and is conducting large-scale environmental assessments to identify high-risk contamination zones. In India, policymakers are in the early stages of creating national PFAS regulations, with a focus on preventing PFAS discharge from large-scale manufacturing plants. Both countries are also investigating sustainable methods for managing PFAS-contaminated waste to prevent further environmental damage.
5-2. Challenges in Regulation
Despite these efforts, regulating PFAS is difficult because:
- Thousands of different PFAS chemicals exist.
- They are used in many industries.
- Effective removal methods are still being developed.
- Some PFAS substitutes may also have unknown risks.
6. How Can We Reduce PFAS Exposure?
6-1. What You Can Do
While governments work on regulations, individuals can take steps to minimize PFAS exposure:
- Filter Your Water: Use activated carbon or reverse osmosis filters.
- Choose PFAS-Free Products: Look for labels indicating “PFAS-free.”
- Avoid Non-Stick Cookware: Opt for stainless steel or cast iron instead.
- Be Cautious with Food Packaging: Reduce fast-food consumption and avoid grease-resistant wrappers.
7. The Role of Advanced Evaporation Technology
Scientists and industries are actively developing safer ways to manage PFAS research and its environmental impact. Advancements include improved filtration systems, innovative chemical treatments, and bioremediation techniques that use microorganisms to break down PFAS. While Smart Evaporator™ does not directly remove PFAS, it plays a crucial role in supporting laboratory workflows by providing efficient solvent evaporation solutions. This enables researchers to conduct experiments more effectively and contributes to advancements in chemical and environmental studies.
Learn More About Smart Evaporation Solutions
Addressing PFAS contamination requires ongoing research and advanced technology. Learn how Smart Evaporator™ enhances solvent evaporation in laboratory research, supporting scientists in tackling various analytical and experimental challenges.
Visit the Smart Evaporator™ Page
8. Conclusion: The Future of PFAS Management
Moving Forward in PFAS Regulation and Research
As awareness of PFAS contamination grows, governments, industries, and researchers are working together to find solutions. Stricter regulations are being enforced worldwide, pushing industries to innovate and transition toward safer alternatives. Continued research is critical to understanding long-term exposure effects and developing effective remediation strategies.
The Role of Technology and Innovation
Advancements in filtration, bioremediation, and chemical treatment are improving our ability to detect and mitigate PFAS contamination. While challenges remain, emerging technologies provide promising solutions for safer industrial processes and environmental restoration efforts.
Collective Action for a Safer Future
Reducing PFAS contamination requires a collaborative effort between policymakers, industries, researchers, and consumers. By staying informed, supporting regulatory measures, and adopting safer alternatives, we can mitigate the risks associated with PFAS and protect both human health and the environment.
Discover the Smart Evaporator™: The Safer, Simpler Solution for Solvent Removal
Sources
This article is based on information from reputable sources, including:
- Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) reports and guidelines (updated 2024)
- European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) regulatory updates (latest revisions as of 2024)
- Research studies on PFAS contamination and health impacts published in peer-reviewed journals (2023-2024)
- Governmental publications and official reports from Japan, South Korea, Australia, Canada, China, and India (2023-2024)
- World Health Organization (WHO) reports on PFAS and public health (2024)
- Reports from non-governmental environmental organizations such as the Environmental Working Group (EWG) and Greenpeace, which have been actively monitoring PFAS pollution trends and advocating for stricter regulations (2023-2024)

