Retronasal Aroma Analysis of Green Tea
Purpose
Green tea was analyzed using a multipurpose ChemZo ion source.

Methods
| Ion Source | ChemZo (BioChromato) |
| Mass Spectrometer | compact QTOF (Bruker) |
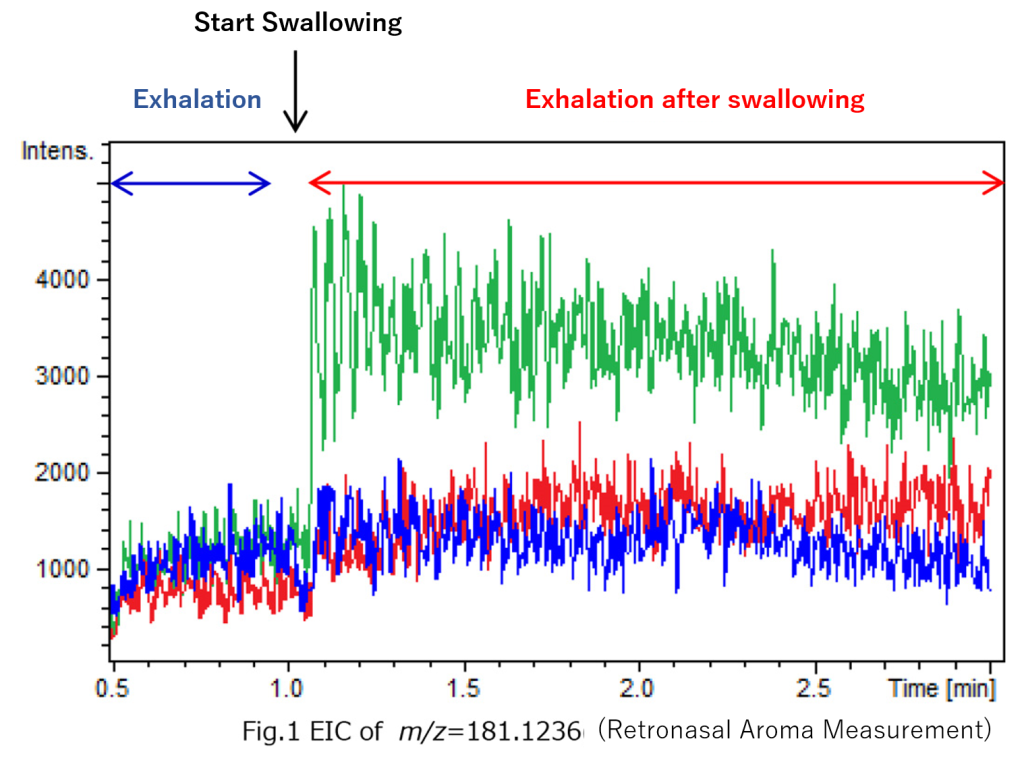
| Measurement Method | Three types of tea—matcha (green), tea bag A (red), and tea bag B (blue)—were swallowed (60 mL each), and exhalation was measured for 2 minutes. |
| Data Processing | The Retronasal Plus feature of Spectra Scope was used to determine whether distinctive aromatic components could be detected from the three types of tea. |
Results
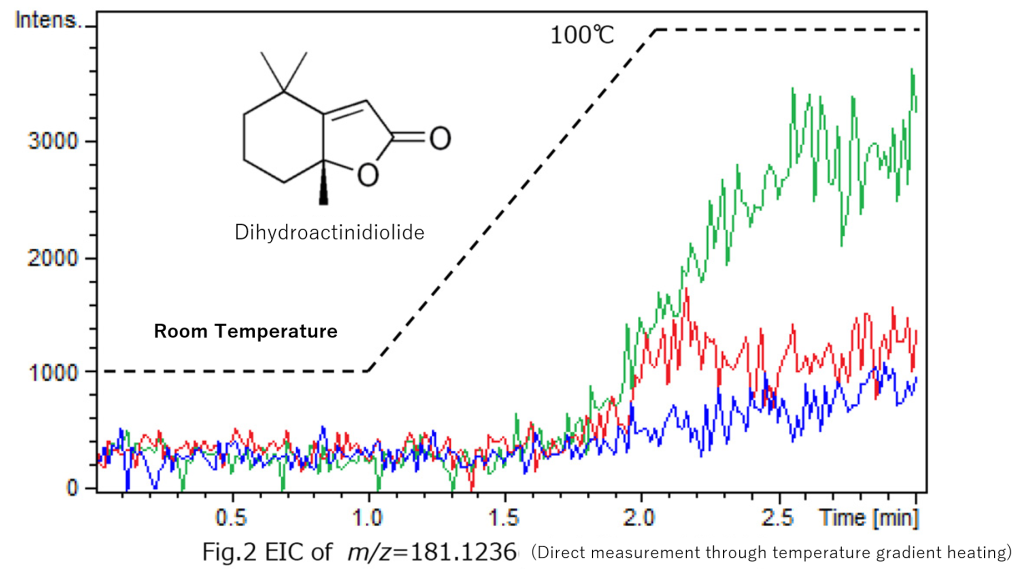
An ion with m/z = 181.1236 was strongly detected from matcha. Composition analysis identified it as C₁₁H₁₆O₂, which was presumed to be dihydroactinidiolide, a component found in tea. Results from temperature-gradient heating showed that the marker molecule was detected at higher temperatures, suggesting that it lingers in the mouth for an extended period after swallowing during retronasal aroma measurement.
Since ChemZo supports the measurement of gases, liquids, and solids, retronasal aroma analysis was conducted directly while swallowing the food. Subsequently, the identified marker ion could be confirmed via direct measurement using temperature-gradient heating without any preprocessing.