Comparative Analysis of Laser Printer Printed Materials
Purpose
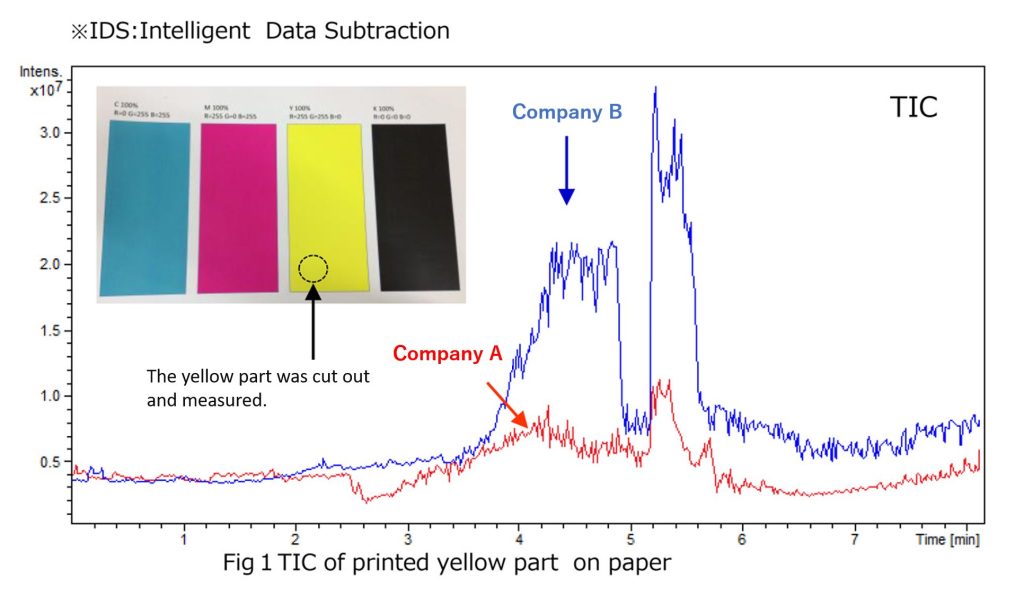
A comparative analysis of the yellow-printed sections of two laser printer models was conducted using a time-of-flight mass spectrometer as the detector.
Methods
| Ion Source | ChemZo (BioChromato) |
| Mass Spectrometer | compact QTOF (Bruker) |
| Measurement Method | Yellow color codes were printed and cut into 3 mm diameter circles. Two samples were analyzed by heating from room temperature to 600°C using a temperature gradient device. |
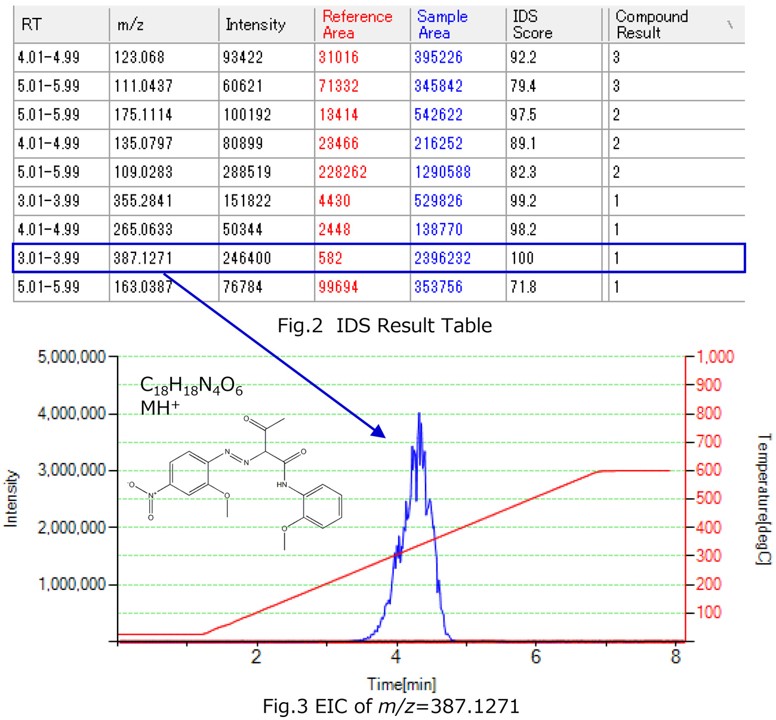
| Data Processing | The differences between the samples were examined using the IDS* (automatic differential processing function) of Spectra Scope. Composition analysis was performed on peaks with differences, and compounds were estimated using the Compound Search database. |
Results
Fig. 1 shows the TIC of Company A (in red) and Company B (in blue). Differential analysis was performed using the IDS function in Spectra Scope, revealing differences in multiple compounds (Figs. 2 and 3). Among these differences, m/z = 387.1271 was detected in the print sample from Company B around 4 to 5 minutes (300–400°C), with composition analysis suggesting a match with C18H18N4O6. The compound was suggested to be “Pigment Yellow 74” using Compound Search. ChemZo enabled direct analysis of printed materials without any sample preparation, allowing straightforward differential analysis and the suggested identification of compounds.